-
LEO, MEO, GEO: Operators Chart the Multi-Orbit Path Forward
Comments Off on LEO, MEO, GEO: Operators Chart the Multi-Orbit Path Forward- Posted by icasat
- 10 January 2024
- News

Deep-water drilling is often a $10 million a day, mission-critical operation. If a signal drops, and an oil rig engineer can’t track their machinery for more than a few seconds, they have to shut down operations — or risk the safety of their crew .Safety is a priority — but that’s a lot of money down the drain.
With the importance of connectivity at the forefront, more and more oil, gas, and other industry players are relying on satellites to beam high-speed internet services to the job sites. Yet while satellite has been traditionally viewed as a backup to fiber, its role is starting to shift into a first line of defense.
As such, satellite service providers like Houston-based Speedcast, one of the world’s largest global connectivity providers specializing in managed communications for business and enterprise networks, are unveiling service offerings that blend signals from multiple orbits across Low-Earth Orbit (LEO), Medium-Earth Orbit (MEO), and Geostationary Orbit (GEO), as well as terrestrial networks. The company says this is the best way to ensure connectivity is truly seamless when dollars are at stake.
“If something goes down, an energy operator has to shut down the drilling operation because they’re running things remotely, all the way back in Houston or Aberdeen and the operation might be 300 kilometers off the coast of Angola,” says Speedcast CEO Joe Spytek. “That’s why they have always been willing to pay a premium for high-quality, high-availability services.”
Spytek says the concept of 100 percent uptime is now a reality. “We weave together the largest global footprint of GEO capacity, while also integrating mPOWER links or a Starlink terminal, blending all the connectivity paths together so if one were to go down, the customer still maintains their network communications,” he says.
When Spytek took the helm of Speedcast in 2021 as the company emerged from bankruptcy, he set out to transform how Speedcast did business, positioning the company for a multi-orbit future of software-defined networks.
One of Speedcast’s more recent moves was a partnership with SpaceX’s Starlink constellation. Speedcast was the first announced integrator for Starlink. As the demand for multi-orbit, or “multipath” satellite connectivity — between GEO, MEO and LEO — Spytek says his inbox is loaded with inbound queries from organizations with land, maritime, energy and government operations.
“With access to LEO constellations now, we’ve been able to access whole new customer segments,” says Spytek. “A Starlink terminal is more like a terrestrial LTE service than a satellite service in some respects. When you pair Starlink with a customer’s existing terrestrial service, you can actually offer a very highly reliable network. We’ve already added hundreds of new customers on the back of some of these LEO offerings. That’s really one area where we’re seeing very strong growth.”
There’s plenty of room for other winners, it seems, as the industry migrates toward an expanded vision of satellite connectivity, driven by the ability for satellites in different orbits to communicate with each other. As operators merge and adopt more sophisticated ground terminals that can relay signals across multiple constellations, it’s clear the industry is on a multi-orbit trajectory. All of this raises questions about the new market opportunities and use cases for this next level of seamless satellite connectivity.
The Big Picture
The rollout of multi-orbit satellite networks seems to have happened overnight, but the process actually happened gradually in response to increasing demand for high-speed, low-latency, reliable satellite connectivity. Today, operators and service providers are looking for ways to differentiate themselves, while evaluating the ground equipment partnerships that will enable them to truly support connectivity across multiple orbits.
NSR, an Analysys Mason company, estimates that the non-GEO share of total high-throughput capacity demand will grow from approximately 21 percent in 2022 to about 52 percent in 2032. Valour Consultancy expects global shipments of communications on the move (COTM) flat panel antennas to grow from a very low base of just below 3,000 to approximately 100,000 units by 2030, at a CAGR of 57 percent.
The conversation around satellite service connectivity has shifted, says Maxime Puteaux, principal advisor for Euroconsult.
“Compared to a few years ago, when there were debates about LEO versus GEO, the answer [now] is actually ‘in between and multi-orbit,’” says Puteaux. He says many operators now consider GEO, MEO, and LEO together as there is no one single solution that fits all of their needs.
“There is a shift from end user use cases from pure broadcast, or a one-way signal, to more data-centric use cases which require two-way communications. Operators are moving and are diversifying towards an architecture which is by far more complex, but which is more suitable for their needs,” he adds.
As the first multi-orbit terminals that can speak to satellites in different orbits are in development now, Blane Boynton, vice president of Product Development for Intelsat, says we can expect to see a handful enter the market at the end of 2023 or early 2024.
“The first-generation terminals will be capable of talking to one orbit at a time and will employ fast switching to move between satellite networks,” Boynton tells Via Satellite. “We believe this fast switching can be transparent to customer use cases. Second generation terminals will take advantage of innovation in electronically steered array technology and will utilize intelligent network routing in the form of edge virtual network functions to achieve simultaneous connectivity into both orbits and networks.”
When these capabilities are realized, he adds, use cases and traffic can be optimized in real time to intelligently route traffic to the network of best service.
“Imagine if streaming media traffic could transit a GSO link while highly interactive traffic like live video conferencing was making use of a lower-latency NGSO network,” says Boynton. “Here you get the best of both worlds. [We] believe this is a key differentiator of the multi-orbit strategy.”
Mission-Critical Services
As the cost of blending multiple orbits for seamless connectivity is technically complex, and it’s costly as well. For these reasons, the initial applications for multi-orbit services support high-stakes use cases — where seamless connectivity is imperative.
In addition to mission-critical energy industry use cases, government and military applications are markets ripe for multi-orbital offerings, says Puteaux.
“Trunking is a good and significant opportunity — blending into ground networks. 5G is supposed to make things easier,” says Puteaux. “Government connectivity definitely is something of interest, and so is maritime and aircraft. If someone needs to fit a specific solution into specific needs, multi-orbit is a way to go. At the end of the day, it needs to fit in with their cost structure so the system remains affordable, which is not so easy to do.”
Mike Pigott, executive vice president of Connectivity at Anuvu, said that as new LEO services and existing GEO markets evolve, Anuvu expects to flex into new markets.
“We think the customers that will want multi-orbit solutions are those who want the best available and most consistent performance over the entire globe,” Pigott says. “Beyond any particular market, we think most mobility connectivity customers want those things today and will want them even more in the future.”
John-Paul Szczepanik, CTO of All.Space, noted that multi-orbit networks offer the benefit of enhanced network resilience — and assurance of uninterrupted services—which is paramount for government clients like the U.S. Department of Defense. He highlights other potential use cases like telecommunications and high-speed internet access to remote, underserved areas, as well in-flight internet services, maritime, and Earth observation.
He spoke to the benefits for national security: “The advent of near-peer rivals in space has revolutionized how we approach space communications and security,” Szczepanik says. “Multi-orbit services are emerging as game-changers in this rapidly evolving landscape, offering many benefits across various industries and markets. Multi-orbit services guarantee the uninterrupted operation of command-and-control networks, which is critical for national security.”
From the Ground Up
The importance of ground equipment and integration cannot be overemphasized to enable multi-orbit connectivity. A handful of equipment manufacturers are making news for rolling out technology that supports hybrid networks.
Anuvu, for example, recently tapped Telesat to provide antennas and ground station infrastructure to support its multi-orbit network, as enterprise customer needs evolve beyond GEO and LEO connectivity. Anuvu has ordered eight MicroGEO satellites from Astranis, which are smaller than a traditional GEO satellite. Anuvu also has an agreement with Telesat to utilize its Lightspeed LEO constellation in the future.
Pigott says the company strongly believes multi-orbit solutions will be the global norm in the next five to 10 years.
“We have a long history in serving global mobility customers with GEO satellites and our new Anuvu constellation comprised of MicroGEOs will continue our efforts to utilize new technology,” said Pigott. “We have adopted a multi-orbit strategy and believe Telesat’s Lightspeed LEO constellation is going to serve that future as well. Hybrid multi-orbit networks simply make the most sense for what we think will be core requirements of customers for their mobility networks — high performance high reliability, flexibility of service, and ultimately a superior quality of experience.”
All.Space, meanwhile, is focusing on enabling multi-orbit services from the ground up, with its ‘smart terminal’ range.
Across the Globe
Japanese satellite communication provider Sky Perfect JSAT is also eyeing a multi-orbit future, with the launch of a joint venture with Japanese telco NTT called Space Compass.
The company is in strategic discussions with LEO satellite companies to explore partnership opportunities, says Hiroyuki Yagihashi, general manager of Sky Perfect JSAT’s NTN Business Division, Business Innovation Group, Space Business Unit.
“Regarding our potential partnership, it's important to note that our mission is not just to resell internet access service, but to enhance the user experience with multi-orbit infrastructure,” Yagihashi says.
In multi-orbit services, it is important to offer not only communications services, but also value-added solutions to solve customer problems, he added.
“Partnerships with solution providers for security features and vertical applications will be necessary,” says Yagihashi, “In addition, it is important to work with partners that provide distribution channels to reach global markets.
Like other stakeholders, Yagihashi believes adoption of multi-orbit is still in its infancy, with SD-WAN technology performing traffic control and multi-orbit services. But JSAT sees a large adoption in the future, and integration into 5G.
“We believe that multi-orbit will be widely adopted in 10 years, because a robust and ubiquitous network is the strongest demand from users and MNOs around the world, and multi-orbit is the only method to solve the aforementioned needs,” said Yagihashi. “We believe that in the long term, multi-orbit control will be realized using 3GPP specification technology, which will be standardized as ‘5G-Advanced’ by 2026.” VS
Marisa Torrieri is a freelance writer from Washington, D.C.
-
SpaceX Aims to Offer Starlink Direct-to-Cell Text Service in 2024, IoT By 2025
Comments Off on SpaceX Aims to Offer Starlink Direct-to-Cell Text Service in 2024, IoT By 2025- Posted by ENoohi
- 27 November 2023
- News
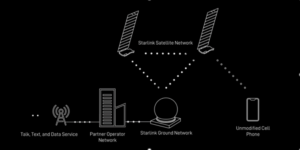
Graphic of Starlink’s direct to cell function. Photo: SpaceX
SpaceX is targeting direct-to-cell service that enables text messaging with the Starlink constellation in 2024, and voice and data and IoT service by 2025. SpaceX updated Starlink’s website with a new page focusing on direct-to-cell service.
SpaceX Chief Engineer Elon Musk previously gave the target that Starlink would enter beta service for direct-to-cell with T-Mobile in late 2023.Starlink announced the deal with T-Mobile last year, pitching the service as a way to close gaps in cellular networks in rural and remote areas and allow T-Mobile customers to send messages via Starlink satellites.
Starlink has signed a number of other global cellular providers as partners — Rogers in Canada, Optus in Australia, One NZ in New Zealand, KDDI in Japan, and Salt in Switzerland.
Starlink is encouraging other cellular providers to reach out to use the service to expand their networks. Starlink satellites will use partner spectrum to operate the service over their respective countries.
Explaining the service, the website says that Starlink satellites with direct to cell capability have an onboard eNodeB modem that functions “like a cellphone tower in space, allowing network integration similar to a standard roaming partner.”
SpaceX also said that direct to cell satellites will initially be launched on Falcon 9, then Starship. “On orbit the satellites will immediately connect over laser backhaul to the Starlink constellation to provide global connectivity.”
This confirms that SpaceX plans to offer IoT service as well as text, voice and data over satellite. SpaceX said that direct to cell will connect IoT devices with common LTE standards. Earlier this year when subsidiary Swarm stopped selling new IoT devices, its website said it will eventually offer an LTE version of its modem that is compatible with Starlink’s direct to cell network. -
There’s been an uptick in burned Starlink satellites over the summer, according to satellite tracking data
1 Comment- Posted by ENoohi
- 27 September 2023
- News
Date:09/20/2023
Starlink, a satellite constellation operated by aerospace company SpaceX, lost 212 satellites in the period spanning July 18th and September 18th, data compiled by satellitemap.space shows.
Data shows the number of burned-up satellites steadily increasing over the past three years, but a significant spike can be observed starting the month of July.
It’s unclear whether these satellites were scheduled to de-orbit or whether the burn-ups were a result of a failure. Cybernews has reached out to SpaceX for comment but has not received a response.
Some experts questioned the accuracy of numbers posted on the tracker website, saying they appeared to be unusually high. According to satellitemap.space, its data is based on public tracking information published on space-track.org and elsewhere
Starlink satellites are designed to burn up in the Earth’s atmosphere at the end of their life cycle, which is approximately five years.
SpaceX started launching Starlink satellites in 2019. Over 5,000 have been sent into Earth’s lower orbit since then. Of those, about 4,500 are believed to be active.
Satellites can also be vulnerable to electromagnetic storms, with strong solar flares recorded this summer as the sun enters a period of heightened activity.
Destructive solar events have affected Starlink before. In February last year, SpaceX said it lost 40 new satellites shortly after launch because of an electromagnetic storm. When accounting for the rocket launch, it potentially cost the company about $100 million in damages.
Reference: https://cybernews.com/
-
Iranian-American scientist Elham Tabassi has been recognized by the Time magazine as one of the 100 most influential people in artificial intelligence (AI).
2 Comments- Posted by ENoohi
- 23 September 2023
- News
Date:09/07/2023
Born and raised in Iran, Tabassi says she always dreamed of being a scientist. She graduated in electronics from Sharif University of Technology in Tehran and then immigrated to the US to continue education in 1994 and began working at the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) five years later on various machine-learning and computer-vision projects with applications in biometrics evaluation and standards.
Earlier in her career, she was the principal architect of NIST’s Fingerprint Image Quality (NFIQ), now an international standard for measuring fingerprint image quality, which has been deployed by the FBI and Department of Homeland Security.
Nearly five years ago, the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) began building a program to advance the development of trustworthy and responsible AI systems. It was Elham Tabassi, an electrical engineer and chief of staff of the institute’s IT lab, who pitched moving the conversation about the impact of AI from principles to practical policy implementation.
Her suggestion proved markedly consequential. After Tabassi’s team started doing research around AI security and bias, Congress mandated NIST (part of the Commerce Department) to develop a voluntary risk-management framework for trustworthy AI systems as part of the National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) of 2021.
She proceeded to lead that effort, and in January 2023 unveiled the final framework designed to help users and developers of AI analyze and address the risks associated with AI systems while providing practical guidelines to address and minimize such risks.
The 2023 TIME100 AI list also features 99 other people, like CEOs, founders and co-founders, including Elon Musk of xAI, Sam Altman of OpenAI, Andrew Hopkins of Exscientia, Nancy Xu of Moonhub, Kate Kallot of Amini, Pelonomi Moiloa of Lelapa AI, Jack Clark of Anthropic, Raquel Urtasan of Waabi, Aidan Gomez of Cohere and more.
Reference: https://time.com/, https://ana.press/#AI #Elham Tabassi #Artificial inelligence
-
- Posted by icasat
- 08 December 2019
- News
Today, we are thrilled to announce that ST Engineering’s acquisition of Newtec is officially complete – and we welcome Newtec into ST Engineering as part of our Satellite Communications (satcom) business within ST Engineering Electronics. Over the coming months we will integrate Newtec’s business with that of ST Engineering iDirect.
This bold move brings two satellite industry leaders together establishing a dynamic new powerhouse to serve your biggest ambitions. Our goal is to create the world’s most advanced satellite ground capabilities – uniting our technology heritage and passion for innovation – to deliver much more to you than we ever could before.
Now, as one combined business group, we will execute a streamlined process to fully integrate the two entities, covering business operations, sales and marketing, and the corresponding product portfolios, with the result being a unified go-to-market strategy and over time a converged technology offering.
Over the next 90 days we will conduct a joint deep dive into our combined products and technologies. This will enable us to identify the best offerings from both entities and options for leveraging them in ways that most effectively address our customers’ needs.
To drive higher brand visibility and position the company for greater commercial impact and marketing presence, Newtec will be renamed as ST Engineering iDirect (Europe) NV. In line with the name change, it will adopt ‘ST Engineering’ as its corporate brand. Both changes take effect from 3 October 2019.
As we integrate, we will make decisions in our combined customers’ best interests based on these priorities:
- Commitment to converged technologies and unified roadmap. We will maintain the two product brands, iDirect and Newtec, during our integration phase. As we work towards a unified technology strategy and product offering, we will consult with you to determine the best product fit for your future needs.
- An enhanced and integrated product portfolio. We are combining best-in-breed technologies – iDirect’s unparalleled networking and mobility features with Newtec’s ground-breaking innovations in performance and efficiency – and will offer converged technologies that will lead our industry forward and deliver the best possible solutions to the market.
- Customer investment prioritized. Many of you utilize both iDirect and Newtec platforms, which delivered the best technology for your applications. Your investments will be prioritized to ensure the most optimal path for you so that you realize the benefits of the combined entity with minimal operational disruption.
- Expanded access to accelerate your growth. You will gain access to a partner that offers you the scale you require to succeed in this transforming market; one with a wider breadth of integrated capabilities and offerings that can proactively anticipate and better meet your needs across multiple market segments.
- Quicker time to market with new innovation. With our combined strengths, scale, common vision and focused approach, we will be able to accelerate our time to market and deliver solutions to you in the time frame that a transforming industry demands.
Through all these advances, you will continue to receive the same high-quality level of service and solutions as you expect, and with the added peace of mind that they come from one large, trusted and integrated group.
You can anticipate frequent and transparent communications from us validating our key decisions as we bring our technologies together and plan new capabilities. As we go through the integration process, be assured we will provide the best path forward based on whatever technology you have invested in.
This is a pivotal time in our future and in yours. As we become a united force in the market we are thrilled to share our journey and our future success with you.

-
- Posted by icasat
- 13 February 2017
- News
International Communication Age with SATellite also known as ICASAT participated in the greatest ICT information technology industry event in oil & gas market that was held at 29th and 30th January 2017. This event took apart in the Beheshti international university at Tehran.
The exhibition also accompanied with a conference talking about the new directions and technologies in using IT on oil & gas industry.
ICASAT in exhibition section demonstrated the corporation services for oil & gas market providing business grade satellite connectivity for off-shore and land-based telecommunication with advance of internet, intranet and corporate connectivity, VoIP and many others.
ICASAT is a leader company on providing innovations in satellite-based connectivity such as M2M, Ka-band and HTS specially solutions suitable for IoT networks. The company also has one of the biggest teleport sites locating many hub stations to service various vertical market costumers.
In addition to present the company satellite-based connectivity solutions, ICASAT attended to conference by presenting two papers with the titles “the role of satellite communications in the oil and gas industry and its future” and “machine-to-machine communication (M2M) internet-of-things (IoT) via satellite and its application in the oil, gas and petrochemical industry”.
-
ICASAT in TELECOM 2016 Exhibition
Comments Off on ICASAT in TELECOM 2016 Exhibition- Posted by icasat
- 08 January 2017
- News
ICASAT is participating on 17th TELECOM exhibition referring to presenting all of Iranian and foreign companies incorporating on communication, electronic and information basis. The main companies are active in software and hardware devices and application related to different information technology areas specially telecommunication and all the related industries as well. ICASAT as a part of important telecommunication company in Iran and as the biggest satellite-based communication service provider is present at this show. We demonstrated our services to our visitors with main focus on maritime antenna and telecommunication services, and also our wide variety of product for banking and oil & gas markets.
ICASAT with the help of state-of-the-art teleport equipment and high speed infrastructure link communication to Iran and Global wide area networks, and also more than a decade experience in servicing multiple market segments, Is one of the greatest SAP license holder for providing satellite-based communication services in Iran. Our solutions include VSAT telecommunication solutions such as point-to-point SCPC, star and mesh networks with adaptive and high efficiency multiple access technologies like TDM/TDMA, DVB-S2/A-TDMA, MCPC/SCPC and so on. We serve enterprise and governments with advanced satellite-based telecommunication technologies for market sectors such as:
- Maritime
- Oil & gas
- Banking and financial Institutes
- Auto-Deploy antennas for disaster reliefs and crisis management
- Enterprise and private networks
- Satellite internet for all sector markets
- Mining and rural industriesIn this exhibition, we demonstrate to our customers and visitors our KNS marine antennas solutions and latest installations of auto-deploy antennas for satellite communication-on-the-move solutions. Contact us to know more about our latest services with info@icasat.net .
-
- Posted by icasat
- 31 March 2014
- News
ICASAT will attend Irantelecom 2014 fair which is held at the Tehran international fair. ICASAT marketing and sales manager, announced the new technologies and services which are going to be introduced to the visitors like Ka-Band, HTS, Frequency reusing technologies. Meanwhile he invited all people active in different ICT areas to visit ICASAT booth at 8th and 9th hall.